字典树(trie)
一、字典树的概念
字典树,顾名思义,是关于“字典”的一棵树。即:它是对于字典的一种存储方式(所以是一种数据结构而不是算法)。这个词典中的每个“单词”就是从根节点出发一直到某一个目标节点的路径,路径中每条边的字母连起来就是一个单词。
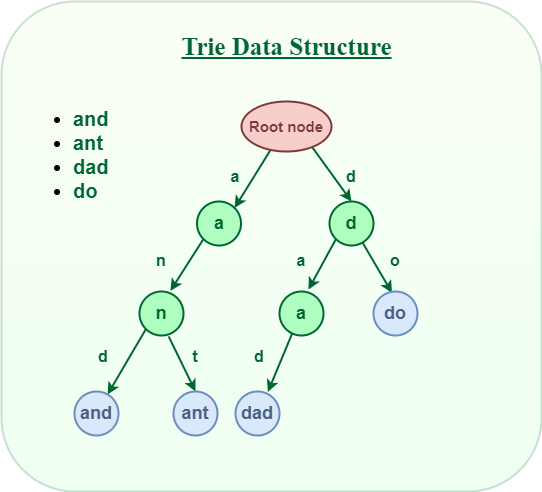
二、字典树的功能
根据字典树的概念,我们可以发现:字典树的本质是把很多字符串拆成单个字符的形式,以树的方式存储起来。所以我们说字典树维护的是”字典“。那么根据这个最基本的性质,我们可以由此延伸出字典树的很多妙用。简单总结起来大体如下:
- 1、维护字符串集合(即字典)。
- 2、向字符串集合中插入字符串(即建树)。
- 3、查询字符串集合中是否有某个字符串(即查询)。
- 4、统计字符串在集合中出现的个数(即统计)。
- 5、将字符串集合按字典序排序(即字典序排序)。
- 6、求集合内两个字符串的LCP(Longest Common Prefix,最长公共前缀)(即求最长公共前缀)。
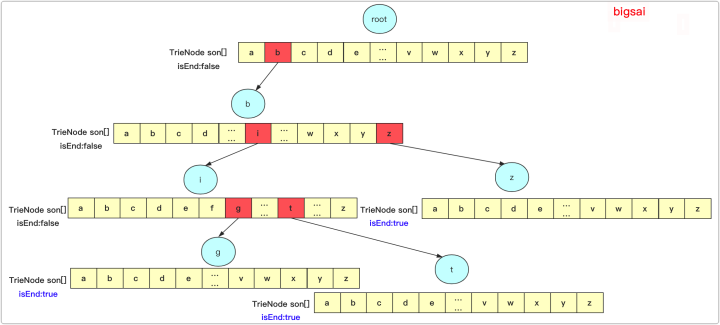
三、字典树的代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; const int ALPHABET_SIZE = 26; // 字母表大小为26个英文字母 // Trie树节点结构 struct TrieNode { struct TrieNode* children[ALPHABET_SIZE]; // 子节点数组,每个节点有26个子节点 bool isEndOfWord; // 标记是否为单词结束 }; // 返回初始化为NULL的新Trie节点 struct TrieNode* getNode(void){ struct TrieNode* pNode = new TrieNode; pNode->isEndOfWord = false; // 初始化为非单词结束 for (int i = 0; i < ALPHABET_SIZE; i++) pNode->children[i] = NULL; // 初始化所有子节点为NULL return pNode; } // 如果不存在则将键插入Trie树,如果键是Trie树节点的前缀,则仅标记叶节点 void insert(struct TrieNode* root, string key){ struct TrieNode* pCrawl = root; for (int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++) { int index = key[i] - 'a'; // 计算字母在字母表中的索引 if (!pCrawl->children[index]) pCrawl->children[index] = getNode(); // 如果对应子节点不存在则创建新节点 pCrawl = pCrawl->children[index]; // 移动到子节点 } // 标记最后一个节点为单词结束 pCrawl->isEndOfWord = true; } // 如果键在Trie树中存在则返回true,否则返回false bool search(struct TrieNode* root, string key){ struct TrieNode* pCrawl = root; for (int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++) { int index = key[i] - 'a'; // 计算字母在字母表中的索引 if (!pCrawl->children[index]) return false; // 如果对应子节点不存在则返回false pCrawl = pCrawl->children[index]; // 移动到子节点 } // 返回当前节点是否为单词结束 return (pCrawl != NULL && pCrawl->isEndOfWord); } // 如果根节点没有子节点则返回true,否则返回false bool isEmpty(TrieNode* root){ for (int i = 0; i < ALPHABET_SIZE; i++) if (root->children[i]) return false; // 如果有子节点则返回false return true; // 没有子节点则返回true } // 递归函数从给定的Trie树中删除一个键 TrieNode* remove(TrieNode* root, string key, int depth = 0){ // 如果树为空 if (!root) return NULL; // 如果正在处理键的最后一个字符 if (depth == key.size()) { // 删除给定键后该节点不再是单词结束 if (root->isEndOfWord) root->isEndOfWord = false; // 如果给定键不是任何其他单词的前缀 if (isEmpty(root)) { delete (root); // 删除节点 root = NULL; } return root; } // 如果不是最后一个字符,则递归处理通过ASCII值获取的子节点 int index = key[depth] - 'a'; root->children[index] = remove(root->children[index], key, depth + 1); // 如果根节点没有任何子节点(其唯一子节点被删除),并且不是另一个单词的结尾 if (isEmpty(root) && root->isEndOfWord == false) { delete (root); // 删除节点 root = NULL; } return root; } // 驱动函数 int main(){ // 输入的键(仅使用'a'到'z'的字母且为小写) string keys[] = { "the", "a", "there", "answer", "any", "by", "bye", "their", "hero", "heroplane" }; int n = sizeof(keys) / sizeof(keys[0]); struct TrieNode* root = getNode(); // 构建Trie树 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) insert(root, keys[i]); // 搜索不同的键 search(root, "the") ? cout << "Yes\n" : cout << "No\n"; search(root, "these") ? cout << "Yes\n" : cout << "No\n"; search(root, "bye") ? cout << "Yes\n" : cout << "No\n"; remove(root, "bye"); search(root, "bye") ? cout << "Yes\n" : cout << "No\n"; return 0; } |
i4683
p4683