散列表冲突的处理(collision handling)
一、挂链法(separate chaining)
当有两个相同的键值时对应的索引相等时,用链表去把他们连起来

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 | /**************************************************************** * 挂链法处理冲突 * Separate Chaining for Collision Handling * date: 2022-5-20 * version: 1.0 * author: ALex Li * **************************************************************/ #include <iostream> using namespace std; struct Link{ int data; struct Link* next; }; struct Link* newnode(int data){ struct Link *p; p=new Link; p->data=data; return p; } struct Link* insert(int data,struct Link* head){ if(head==NULL) return newnode(data); else head->next=insert(data,head->next); return head; } void display(struct Link*head){ if(head!=NULL){ printf("%d->",head->data); display(head->next); } } struct Link*search(int data,struct Link*head){ while(head!=NULL) { if(head->data==data) { // printf("Data Found At address : %p",head); return head; exit(0); } head=head->next; } // printf("Given data not found : "); return NULL; } int main() { struct Link* arr[10]={NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL}; int option,data,x; bool loop=true; while(loop){ cout<<"\nEnter 1 to insert data \nEnter 2 to display hash table \nEnter 3 to search\nEnter 4 to quit "<<endl; cin>>option; switch(option){ case 1: cout<<"\nEnter the integer to be inserted : "; cin>>data; x=data%10; if(arr[x]==NULL){ arr[x]=insert(data,arr[x]); } else insert(data,arr[x]); break; case 2: for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ cout<<"\n %d : "<<i; display(arr[i]); cout<<"(nil)\n"; } break; case 3: cout<<"Enter The Number To Be Searched in hash Table : "; cin>>data; x=data%10; if(search(data,arr[x])!=NULL) cout<<"\t\tData Found At address : %p"<<search(data,arr[x]); else cout<<"\t\tGiven data not found : "; break; case 4: loop=false; break; default: printf("\t\tInvalid Input !!!"); } } return 0; } |
二、开放定址法(open addressing)
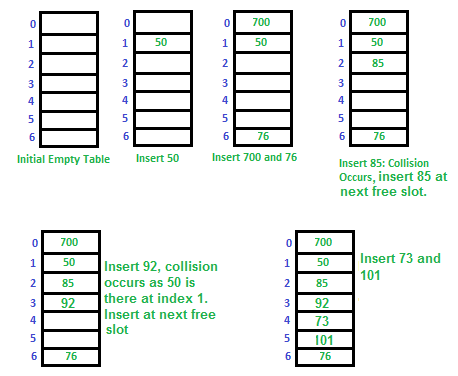
在开放定址法中,所有的元素都被直接存储于散列表中,而非像挂链法一样在每个散列表的位置上再挂出来一条链,如果对应位置已经占用,就尝试下一个空闲位置。
假设我们的哈希函数是对7取模(mod 7),哪么对如下数字操作:50, 700, 76, 85, 92, 73, 101。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 | /**************************************************************** C++ hash open addressing 开放地址法 date: 2022-5-23 version:1.0 author: Alex Li ****************************************************************/ #include<iostream> using namespace std; struct Node{ int data; int status; }; void Insert_new(int data,struct Node hash[]) { int key = data; int i; i = key % 11; if(hash[i].status == 1){ while(hash[i].status == 1){ i++; } hash[i].data = key; hash[i].status = 1; } else{ hash[i].data = key; hash[i].status = 1; } } void Delete_Node(struct Node hash[],int key,int size) { int i=0; while(i<size) { i++; if(hash[i].data==key) { hash[i].status = 0; hash[i].data = 0; printf("\nKey value is deleted\n"); } } } int Search(struct Node hash[],int size,int key) { int i; for(i=0;i<size;i++) { if(hash[i].data == key) { return 1; } } return 0; } void display(struct Node hash[], int size) { int i; printf("Elements in the hash table -> \n"); for(i=0;i<size;i++) { printf(" %d ",hash[i].data); } printf("\n"); } int main() { int size,data,result,option=0; cout<<"Hash table implementation by open addressing method\n"; cout<<"enter the size of the hash table :"; cin>>size; struct Node hash[size]; int i; for(i=0;i<size;i++) { hash[i].status = 0; hash[i].data = 0; } while(option!=5){ cout<<"===============================================\n"; cout<<"1 : Insert an element to the hash table\n"; cout<<"2 : Delete an element from the hash table\n"; cout<<"3 : Search an element in the hash table\n"; cout<<"4 : Display elements in the hash table\n"; cout<<"5 : Exit\n\n"; cout<<"===============================================\n"; cout<<"Enter your choose: "; cin>>option; switch(option) { case 1 :printf("Enter the key to insert :");scanf("%d",&data); Insert_new(data,hash);break; case 2 :printf("Enter the key to Delete :");scanf("%d",&data); Delete_Node(hash,data,size);break; case 3 :printf("Enter the key to Search :");scanf("%d",&data); result = Search(hash,size,data); if(result==1) printf("Searching Success element exits\n"); else printf("serching failed, element does not exits\n"); break; case 4 :display(hash,size);break; } } return 0; } |
Quizzes